| <<< Previous | Index | Next >>> |
Case 8
Clinical and haematological data
77-yr-old woman, suffering from chronic macrocytic anaemia
Hb 55g/l, MCV 109 fl, L 3.1, T 115 G/l
No hepato-splenomegaly.
Serum iron within normal range.
No vitamin deficiency
No inflammatory process.
PB blood smear
RBC: anisopoïkilocytosis, macrocytes, dacryocytes. Granulocytopenia. Platelet anisocytosis.
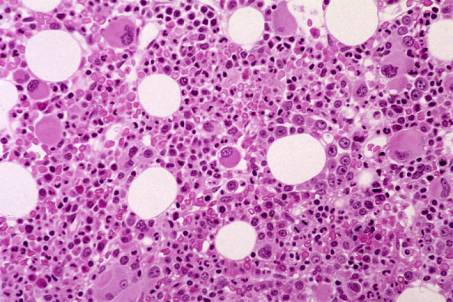
BM aspirate: Hypercellularity. Myelo/erythroid ratio = 1. Increased number of megakaryocytes. Myelodysplasia of the 3 cell lines. No excess of blasts. No ring sideroblasts.
BM histology: Hypercellularity. Erythroid cell line: dyserythropoiesis, macrocytosis. Granulocytic cell line present with shift to the left. Increased number of megakaryocytes with abnormal small forms showing non-lobulated rounded nuclei.
No excess of blasts. No significant fibrosis.
IHC: small excess of CD34+ cells (5-10%) .
Interpretation and diagnosis : hyperplastic BM with dysplastic features (dysmegakaryopoiesis) strongly suggestive of MDS. The chronic macrocytic anaemia together with the morphology of the megakaryocyte raise a suspicion of 5 q - syndrome. Cytogenetics recommended.
Final diagnosis, after cytogenetic analysis : MDS of the 5q- syndrome type
Comments
The 5q- Syndrome is a neoplastic condition belonging to the group of MDS (stem cell clonal disease). Age > 65 yrs, female > male. Refractory anaemia; thrombocytosis +/-. Splenomegaly rare (16 % of the cases). BM exhibiting an increased number of megakaryocytes characterized by non - lobulated nuclei but relatively abundant cytoplasm. Favourable prognosis. Supportive therapy.
BM biopsy is an important part of the clinical work-up of patients with chronic PB cytopenia and suspicion of MDS and has to rule out tumour infiltration or aplastic anaemia as alternative cause of cytopenia.
Remember that myelo
dysplastic
features can be seen in benign and malignant conditions so that the diagnosis of MDS is made by exclusion and the differential diagnosis includes
- nutritional disorders (vit. B12 or folate deficiency);
- dysplastic changes in AIDS or other infection (tuberculosis),
- Dysplastic marrow changes resulting from exposure to toxins and drugs can mimic a MDS (anticonvulsivants, alcohol abuse, antipurines, antipyrimidines, hydroxyurea, cyclophosphamide, procarbazine, acyclovir)
In summary, a combination of data must be taken in account for the correct interpretation of myelodysplastic features in BMB
- Clinical status
- Morphological evaluation of the PB smear, BM aspirate and biopsy specimen
- Cytogenetic analysis .
Case 8. MDS of the 5q- syndrome type.
| <<< Previous | Index | Next >>> |
Copyright 2001, The Author(s) and/or The Publisher(s)
| Organisation: FORPATH asbl |
Coordination: Dr Bernard Van den Heule |
Host: Labo CMP |